Investigating Factors Causes Disorders in Powellem Grass
Called gland disorders may occur due to infection, inflammation, obstruction or tumor. May even appear with acute, chronic or recurrent symptoms. Usually a precise history and proper examination of the patient identifies the primary clues about the cause of the disease, and ultrasound is usually the first option to diagnose them.. Accordingly, inflammation of the salivary glands require urgent referral. In the continuation of the article published today on Dr. Hossein Borjian's website The best dentist in Isfahan It has been compiled for you dear ones. We will study and study the factors that cause disorders in salivary glands.
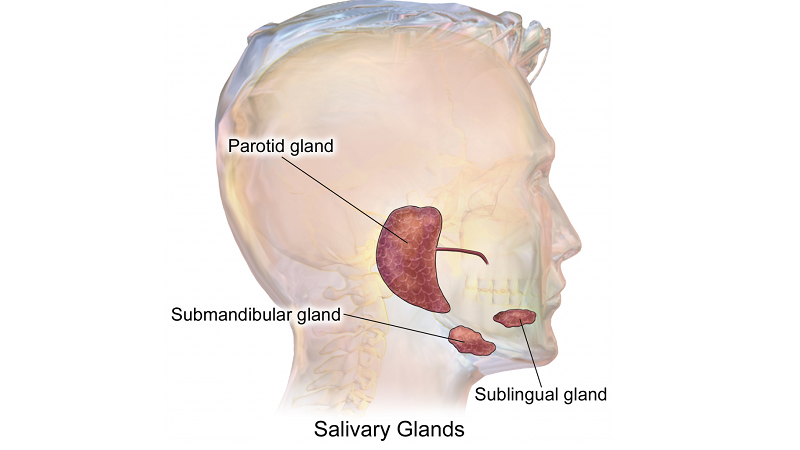
You have three pairs of salivary glands called parotid, submandibular, and sublingual. They are responsible for the production of saliva. Obstruction of the salivary glands are the most common causes of salivary gland disorders. These blocked glands can cause painful symptoms.
Sialolithiasis and sialadenitis
In general, sialolithiasis and sialadenitis may occur in the salivary glands:
- Sialolithiasis occurs when stones made of calcium form in the salivary glands. These stones can block the glands and can partially or completely stop the flow of saliva.
- fluidity (or sialadenitis) It is an infection that affects the salivary glands. This is often due to stones blocking the gland. Staph or strep bacteria can cause this infection. The elderly and infants are more susceptible to this disease.
Suggested content : Duration of using a brace in a child
Sjogren's syndrome
Sjogren's syndrome is another common salivary gland disorder. It occurs when white blood cells target healthy cells of moisture-producing glands such as salivary, sweat, and sebaceous glands.. This condition mostly affects women with autoimmune disorders such as lupus.
viruses
Viruses can also affect the salivary glands. This includes:
- Mumps
- Echo virus
- Influenza virus
- Coxsackie virus
- Cytomegalovirus
- Cancerous and non-cancerous tumors
Even cancerous and non-cancerous tumors may develop in the salivary glands. Cancerous tumors of the salivary glands are rare. When they do occur, it's usually in people, according to Cedars-Sinai 50 until the 60 It happens every year.
Non-cancerous tumors that can affect the parotid glands include pleomorphic adenomas and wart tumors.. Benign pleomorphic adenomas can also develop in the submandibular gland and minor salivary glands, but this is rare..
The causes of inflammation of the parotid glands
The most common cases that may lead to inflammation Parotid glands To be, are:
- Sjogren's syndrome
- Stone in the salivary duct
- Viral parotitis - mumps
- Benign and malignant tumors
- Acute and chronic bacterial parotitis
- Granulomatosis with polyangiitis
- HIV-associated lymphocytic infiltration
- Sarcoidosis, Hereford syndrome with parotid enlargement, fever, anterior uveitis and facial nerve palsy
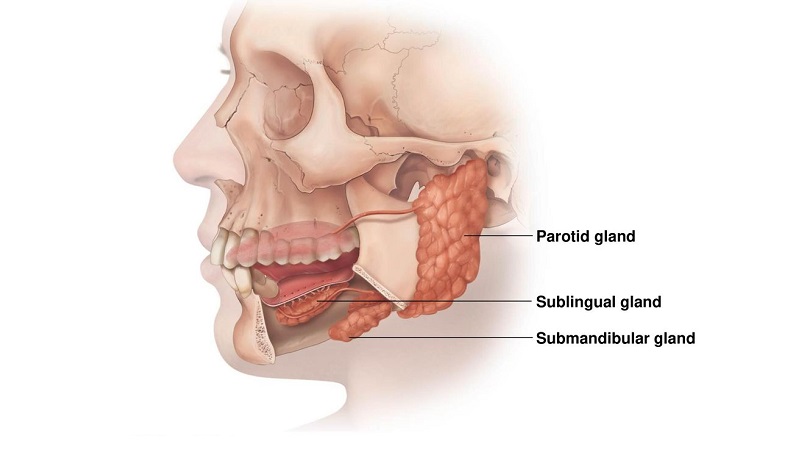
In the submandibular glands, many factors may lead to disorders, including::
- Stone in the salivary duct
- Benign and malignant tumors
- Sjogren's syndrome (It is less common).
But the common causes of minor salivary glands are::
- Mucosal
- Salivary gland infection
- Benign and malignant tumors
Causes
Mumps is the most common cause of salivary gland infection, although the incidence has decreased with the vaccine. Mumps usually causes bilateral inflammation of the parotid glands, although it can be unilateral, and other major salivary glands may be affected in about 10% of cases.. The inflammation lasts about a week and is accompanied by a mild fever and general weakness.
Other viruses that may acutely infect the salivary glands include::
- Herpes
- Parainfluenza
- Influenza A
- Parvovirus B19
- Coxsackie virus
Acute infection
Acute bacterial infection of the salivary glands Infection usually occurs in weak or dehydrated patients. Drug use may inhibit saliva production and increase vulnerability. Before the advent of antibiotics and intravenous fluid rehydration, bacterial parotitis had a high mortality rate.
Chronic infection
In general, chronic bacterial infection can occur in the background of a salivary gland that has already been damaged by stones, radiation, or autoimmune disease.. Chronic infection of the glandular elements destroys the salivary glands and can impair the protective functions of saliva and lead to infections and dental diseases.. As a result, they often go to the dentist first.
Recurrent childhood parotitis
- Frequent episodes of inflammation and pain of the parotid gland with fever and pain, the cause of which is unknown.
- Parotid inflammation is likely to be an early manifestation of HIV infection, and mucocele and oral ranula may also be a manifestation.
- Tuberculosis is a rare cause of parotitis and other inflammation of the salivary glands, but should be considered in people who are immunocompromised or from a high-risk population..
Symptoms of salivary gland infection :
- Then
- dry mouth
- Swelling that is usually painful and tender.
- Decreased mouth opening, difficulty speaking
- Pain in the mouth or face, especially with eating
- Abnormal or bad tastes with purulent secretions from the opening of the salivary duct (Bacterial infection)
Dr. Hossein Borjian's Instagram page The best dentist in Isfahan
The function of the varieties of salivary glands
Approximately 1-1.5 liters of saliva are produced per day by three pairs of major salivary glands:
Sublingual glands
They are located under the tongue and open to the floor of the mouth through several channels. Also a lot (۶۰۰-۱۰۰۰) There are minor salivary glands widely distributed throughout the oral mucosa, palate, uvula, floor of the mouth, posterior tongue, retromolar and peritonsillar regions, pharynx, larynx, and paranasal sinuses..
Saliva is composed of water, electrolytes, lubricants, antimicrobial compounds, enzymes, and growth factors.. Together, these components facilitate speech, chewing and swallowing and start the digestion process. Saliva also prevents problems by protecting the oral mucosa and teeth.
Parotid glands
They are located below the external auditory canal, between the vertical ramus of the lower jaw and the mastoid process. The parotid duct passes through the master and opens through a small papilla on the buccal membrane in front of the crown of the upper second molar.. The parotid gland has a close relationship with the facial nerve, which divides into its branches when passing through the parotid.
Submandibular glands
Pair of walnut-sized structures located below and anterior to the angle of the jaw and wrapping around the posterior edge of the mylohyoid muscle.. Their ducts exit to the floor of the mouth right next to the frenulum of the tongue.
Ways of communication with the specialized dental center of Najm
Attention :
- The scientific accuracy of the above published material should be confirmed by the patient's personal consultation with Dr. Borjian.
- This article is managed and published by the site admin.