Examining and familiarizing with the structure of teeth
In general, knowledge of dental anatomy helps to identify dental problems as quickly as possible and refer for treatment. In this article from Dr. Hossein Borjian's website The best implant in Isfahan We examine the familiarity with the structure of the teeth.
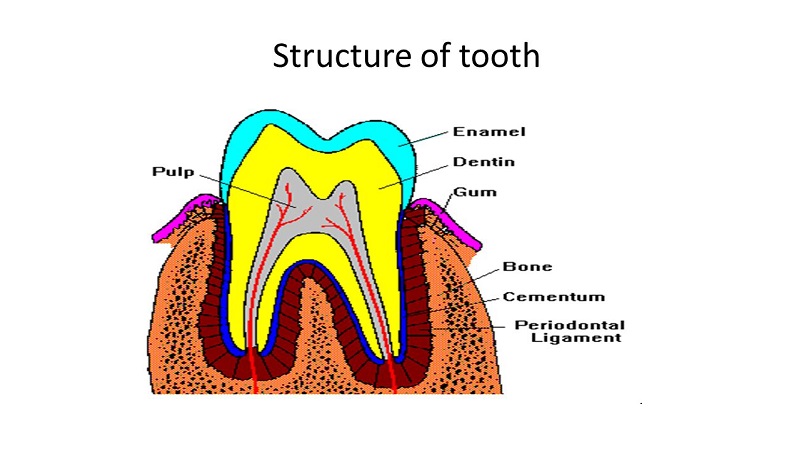
Teeth from enamel, dentin, cementum (cement) and pulp (Tooth pulp) is formed. The part of the tooth that can be seen in the oral cavity is the crown of the tooth, and the part that is under the crown is the root of the tooth. The tooth pulp cavity is located in the center of the tooth, which contains the tooth pulp or its nerves. Root surface of the tooth (Cementum) And the alveolar bone is connected to the fibrous tissue known as the periodontal ligament to prevent impact on the tooth and to absorb and reduce the force on the jaw.. The tooth is held by a tissue consisting of alveolar bone, gum and periodontal ligament.
Mina:
The hardest tissue in the body is tooth enamel, which is dental crown covers. Enamel is as hard as crystal, the hardness of enamel on the Mohs Mineral Hardness Table 7 Is.
ivory:
Dentin is a tissue that forms from the crown to the root of the tooth and is located inside the enamel and cementum. Dentin is always softer than enamel. A small fluid-filled tube called the dentinal tubule passes through the dentin.
Cementum:
The tissue covering the surface of the tooth root is called cement or cementum. Cementum is connected to alveolar bone by periodontal ligament. Cementum is almost as hard as bone.
Dental pulp
Pulp is also called tooth nerve. Blood vessels and lymphatic vessels as well as nerve fibers are located in the dental pulp and deliver nutrients to the dentin..
Periodontal ligament
The periodontal ligament is mainly composed of fibrous tissue that connects the root of the tooth and the alveolar bone.. This ligament does not allow the force applied to the teeth during chewing to be imposed directly on the alveolar bone..
Alveolar bone
The jawbone supporting the tooth is called the alveolar bone in which the tooth is placed. If a large part of the alveolar bone is lost due to gum disease or other causes, the tooth becomes loose..
gum
The soft tissue covering the alveolar bone is called gum.
gingival groove
The gingival sulcus is a small space between the teeth and the gums. The depth of this groove reaches one to two millimeters even in healthy teeth. If this space deepens due to inflammation, a gum pocket or periodontal pocket is created.
Different types of teeth
canine teeth
The canine is the third permanent tooth from the middle of the mouth towards the back, which is present in both the upper and lower jaws. In general 4 fangs, 2 The number in the upper jaw and 2 The number is in the lower jaw, in the mouth. Canines are used to cut food into pieces.
molars
The teeth behind the canine act as a grinder and crush the food. There are two molars in the set of milk teeth, one on the left side and the other on the right side of both upper and lower jaws.. In the set of permanent teeth, two small molars and molars are located on each of the two left and right sides of the upper and lower jaws; That is, in total 16 molars and including wisdom teeth 20 The molars are present in the mouth of an adult.
The number of teeth needed to chew food
The number of permanent teeth is more than milk and most adults 32 They have permanent teeth in their mouths. All permanent teeth generally erupt by adolescence.
Based on the results of the research conducted in the field of the number of remaining teeth in old age and the chewing ability of the elderly, if a person at least 20 Having teeth in the mouth, it can chew most foods. We recommend that you can in old age 20 have one or more teeth, prevent the accumulation of plaque and tartar on the teeth by daily brushing and flossing and periodic scaling and visit the dentist regularly so that the symptoms of dental problems are detected in the early stages and treated in time take action. But if now less than 20 If you have teeth, you can regain the ability to chew by using dental prostheses. So try to take good care of the remaining teeth.
Milk teeth and permanent teeth
The jaw also grows bigger in parallel with the growth of the body. As the jaw grows, permanent teeth replace baby teeth or milk teeth. After all the permanent teeth come in, the chewing power increases and the teeth can crush and crush different foods better.. Permanent teeth are very important and we should use them until the end of our life.
The Instagram page of Dr. Hossein Borjian, the best implant in Isfahan
The contact of primary and permanent teeth
- color: Baby teeth are usually white, while permanent teeth have a yellow tint.
- size: Baby teeth are smaller than permanent teeth.
- Tooth quality: The enamel and dentin of baby teeth are thinner, so baby tooth decay spreads faster..
- The number of teeth: 20 There are temporary teeth in children's mouths, while every adult has them 32 The tooth is permanent.
Timing of growth of permanent teeth
Changing milk teeth into permanent ones happens only once. All baby teeth It occurs between two and three years of age, however, as the jaw bone continues to grow, the balance between the size of the teeth and the jaw is gradually disturbed.. When tissue-dissolving cells form around the roots of baby teeth, the roots gradually decay and become shorter..
After the permanent tooth has grown enough, the baby tooth falls out naturally. to the age 12 All milk teeth fall out at age 28 Permanent teeth replace them.
Attention :
- The scientific accuracy of the above article should be consulted with Dr. Borjian, a specialist, in person Gum and bone grafting be confirmed.
- This article was managed and published by the site admin.
Read more :
Prevention and treatment of dental caries and plaque
Diagnosis of the causes and treatment of bad breath
Medical treatment of tooth and gum abscess